First we need to define each one:
An example of a functional requirement would be:
- A system must send an email whenever a certain condition is met (e.g. an order is placed, a customer signs up, etc).
A related non-functional requirement for the system may be:
- Emails should be sent with a latency of no greater than 12 hours from such an activity.
now we talk about the diferences between them:
In other words, a functional requirement will describe a particular behaviour of function of the system when certain conditions are met, for example: “Send email when a new customer signs up” or “Open a new account”.
A functional requirement for an everyday object like a cup would be: “ability to contain tea or coffee without leaking”.
Typical functional requirements include:
- Business Rules
- Transaction corrections, adjustments and cancellations
- Administrative functions
- Authentication
- Authorization levels
- Audit Tracking
- External Interfaces
- Certification Requirements
- Reporting Requirements
- Historical Data
- Legal or Regulatory Requirements
In other words, a non-functional requirement will describe how a system should behave and what limits there are on its functionality.
Non-functional requirements generally specify the system’s quality attributes or characteristics, for example: “Modified data in a database should be updated for all users accessing it within 2 seconds.”
A non-functional requirement for the cup mentioned previously would be: “contain hot liquid without heating up to more than 45 °C”.
Typical non-functional requirements include:
- Performance – for example: response time, throughput, utilization, static volumetric
- Scalability
- Capacity
- Availability
- Reliability
- Recoverability
- Maintainability
- Serviceability
- Security
- Regulatory
- Manageability
- Environmental
- Data Integrity
- Usability
- Interoperability
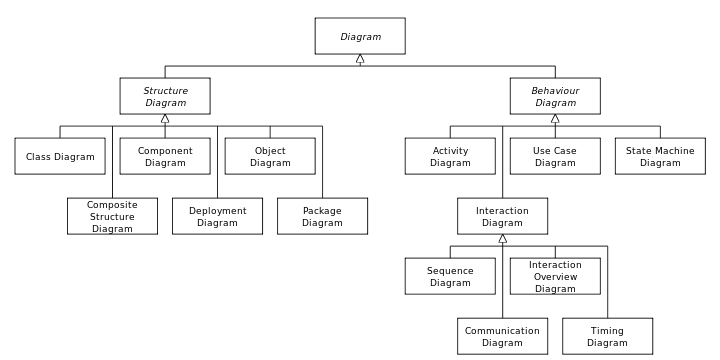 The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental, modeling language in the field of software engineering, that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental, modeling language in the field of software engineering, that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. Software application architecture is the process of defining a structured solution that meets all of the technical and operational requirements, while optimizing common quality attributes such as performance, security, and manageability. It involves a series of decisions based on a wide range of factors, and each of these decisions can have considerable impact on the quality, performance, maintainability, and overall success of the application.
Software application architecture is the process of defining a structured solution that meets all of the technical and operational requirements, while optimizing common quality attributes such as performance, security, and manageability. It involves a series of decisions based on a wide range of factors, and each of these decisions can have considerable impact on the quality, performance, maintainability, and overall success of the application.